Multi-target Build
Sometimes you need build different images for development, serving or other purposes. This guide shows how envd build supports multi-target build.
A build.envd can have multiple build targets. The default build target in build.envd is build:
py
def build():
# ...Create a new build target
New build targets can be defined as functions in build.envd:
py
def build():
# ...
def serve():
# ...Example
envd build -f :<target> executes the build for the given target. Here is an example.
py
def build():
base(os="ubuntu20.04", language="python3")
install.vscode_extensions([
"ms-python.python",
])
configure_mnist()
# Configure jupyter notebooks.
config.jupyter()
# Configure zsh.
shell("zsh")
def serve():
base(os="ubuntu20.04", language="python3")
configure_streamlit(8501)
configure_mnist()
def configure_streamlit(port):
install.python_packages([
"streamlit",
"streamlit_drawable_canvas",
])
runtime.expose(envd_port=port, host_port=port, service="streamlit")
runtime.daemon(commands=[
["streamlit", "run", "~/streamlit-mnist/app.py"]
])
def configure_mnist():
# config.pip_index(url = "https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple")
install.apt_packages([
"libgl1",
])
install.python_packages([
"tensorflow",
"numpy",
"opencv-python",
"matplotlib",
])This demo contains two parts: training a simple digit recognition model using mnist dataset and a webapp to live demo that model.
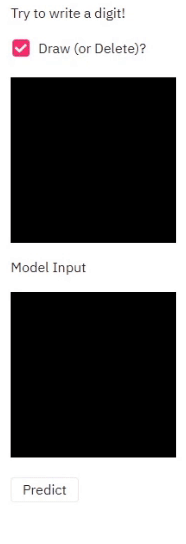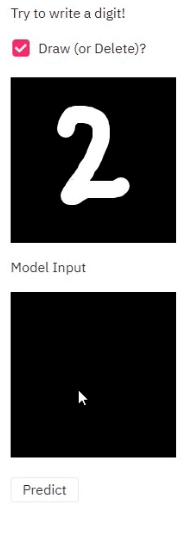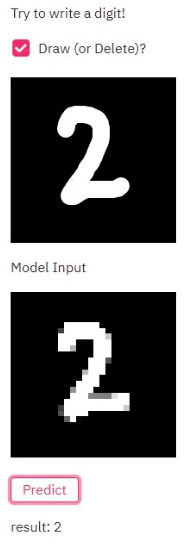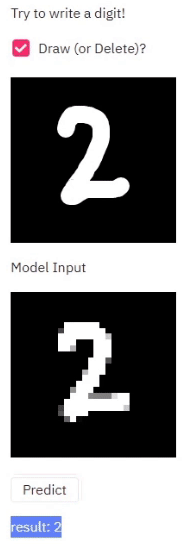
Steps to run the example are shown here.
First create the development environment.
envd upTrain model
Run all the cells of train.ipynb manually.
Run demo web-app
envd up -f :serve